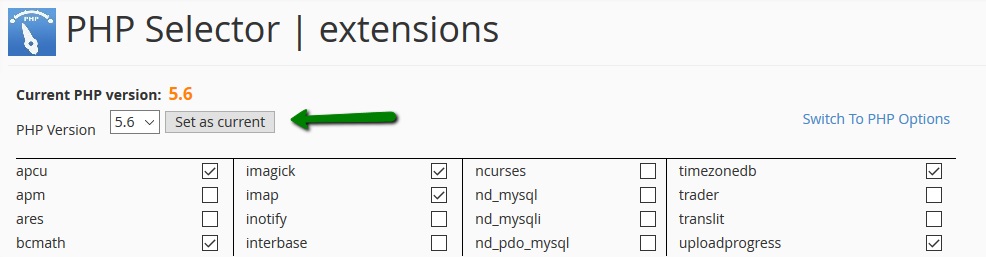
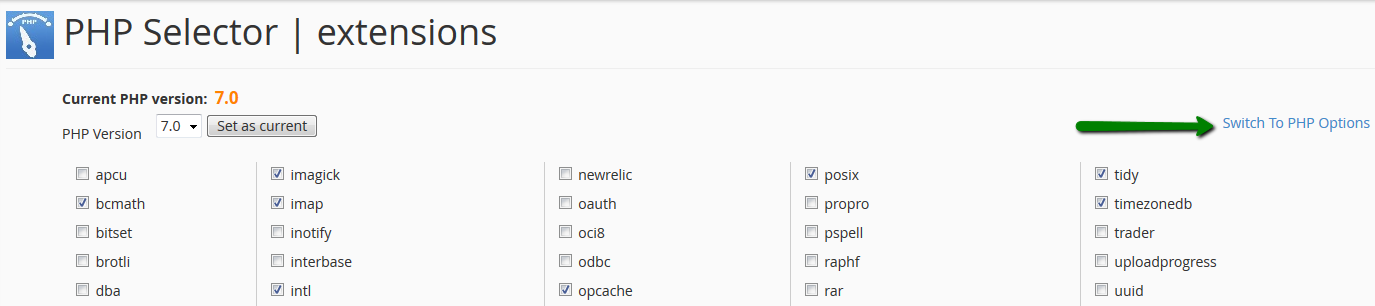
How to manage WordPress website with iPhone application
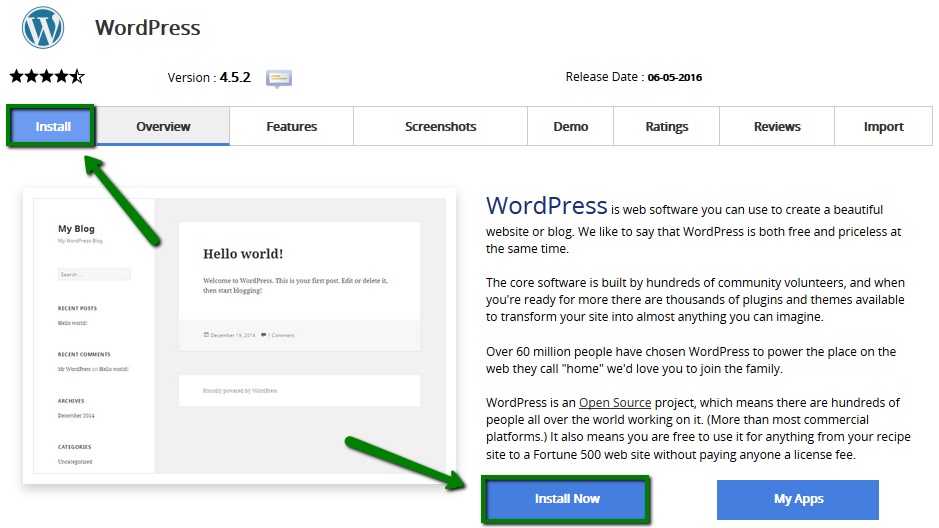
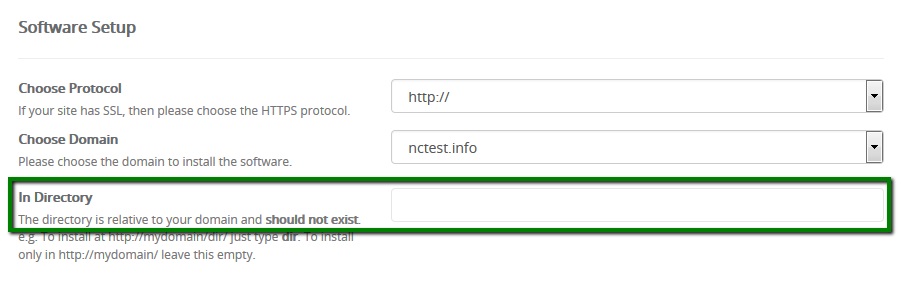
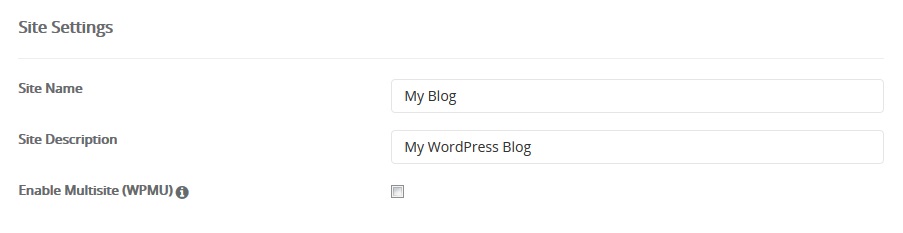
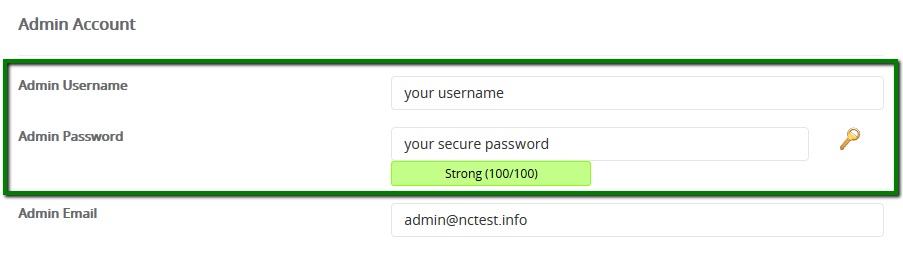
1. In order to be able to manage your WordPress website with an iPhone application, it is required to install the application first. To install the WordPress application, open App Store and go to the Search page. Type ‘WordPress‘ and press Get to install the app:

2. Once it is installed, open the app and press the Log in button:

3. Choose the Log in by entering your site address option:
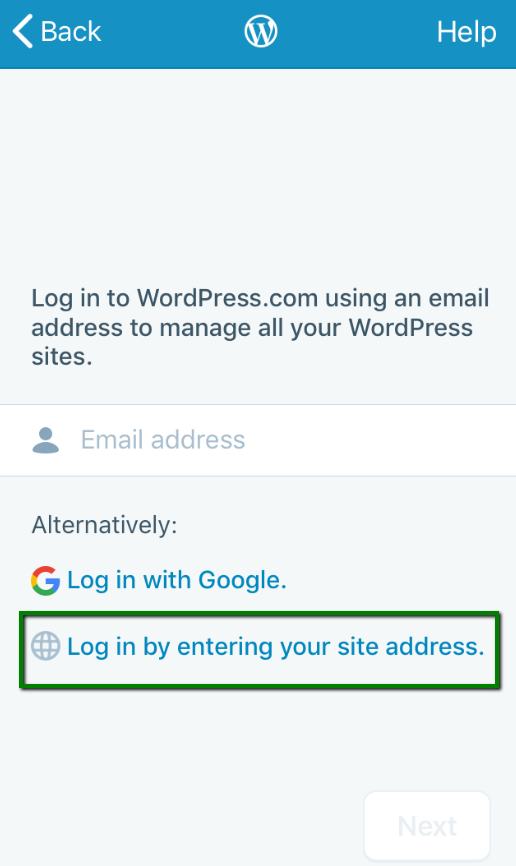
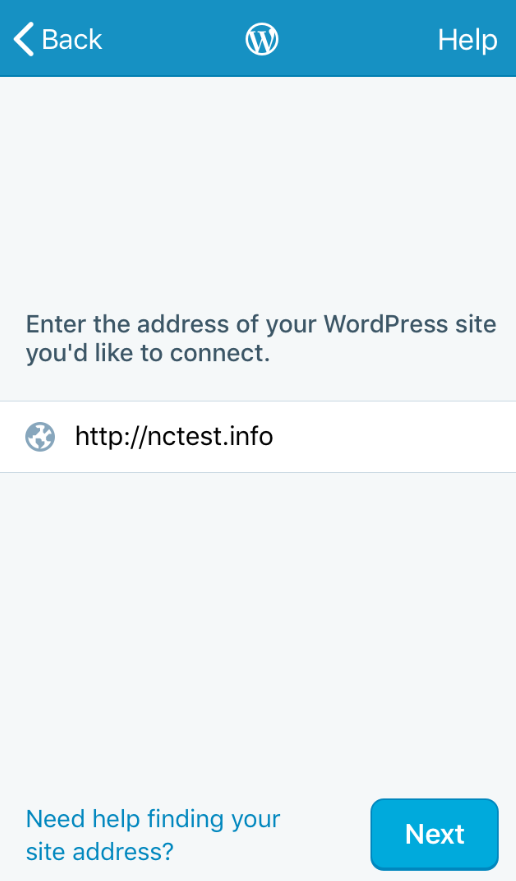
4. Enter your website’s URL:
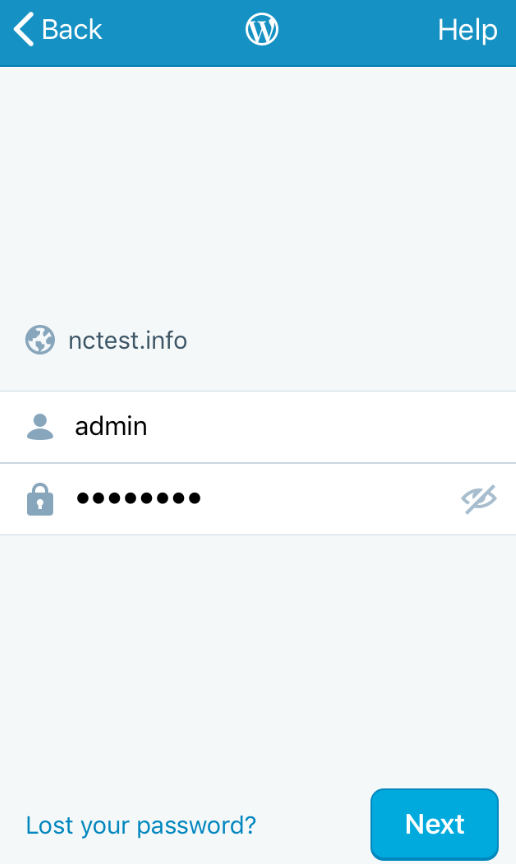
5. Next, enter your WordPress admin account access details:
6. On the next page, you will be able to add more WordPress websites or press Continue to proceed.
After pressing the ‘Continue’ button, you will be redirected to the website management page.
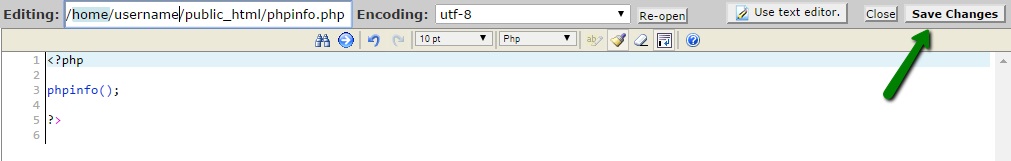
By pressing the ‘Stats’ button, you can install JetPack plugin to track your website’s stats. To install Jetpack, press the Set up Jetpack button:

7. To set up JetPack you will need to enter your email address that is used for your account at wordpress.com (it is required for a JetPack). If you don’t have an account at wordpress.com, create one prior to setting up JetPack. Once JetPack is set up, you will be able to check different statistics for your website, such as Latest Posts Summary, Daily stats, Posting Activity and other.
8. Publish part of the app has the following options:
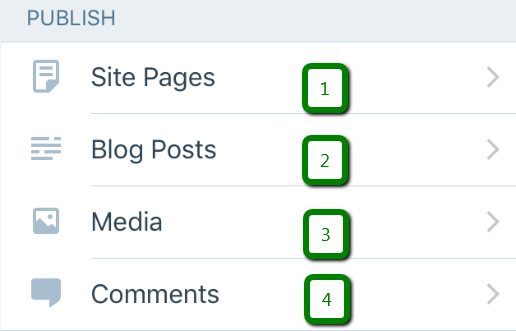
Site Pages menu allows you to:
- create pages by pressing a “+” sign;
- check published, drafts, scheduled and trashed pages;
- search for pages on your website;
- view or move pages either to Draft or Trash by pressing a “…” sign.
Blog Posts menu allows you to do the same things as in the Site Pages menu but with your posts.
A post can be published by pressing the ‘+’ sign
In Media menu you can upload your media content by pressing the ‘+’ sign or ‘Upload media’ Button. You will be able to choose one of the following options:
- take a photo or video to upload to your website;
- choose a photo or video from the library on your phone;
- upload a photo from other Apps (for example from iCloud).
In Comments menu you will be able to check your comments and:
- approve a comment;
- send a comment to trash;
- mark a comment as spam;
- edit a comment.
9. Personalize section. Here you will be able to work on your themes and menus:
Themes menu allows to Customize, check Details and upload themes you have. Additionally, you will be able to install new themes. That can be done by pressing the “…” sign.
In the pop-up window you will see the following options:
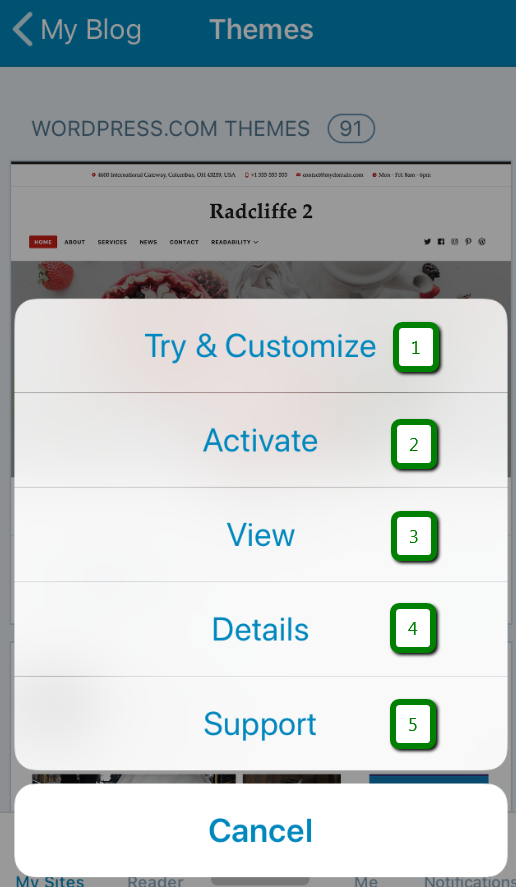
With the Try & Customize option you can ‘play around’ with the theme, test it out to see how it will look like on the website and activate it right away by pressing the corresponding button.
Activate option activates a theme.
View can be used to preview the theme.
Details to check theme details.
Support is where you can contact the theme support.
10. Configure part of the WordPress application dashboard allows you to:
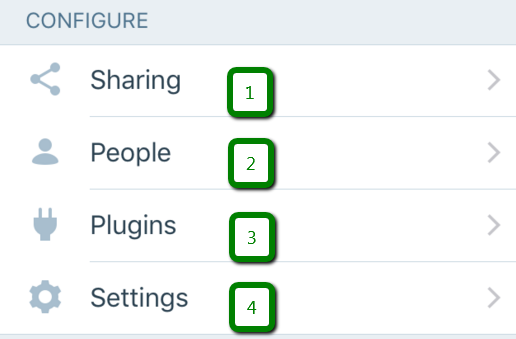
- add and manage Sharing Buttons on a website;
- create new users on a website by pressing the ‘+’ button which is located in the People menu.
- manage your plugins in the corresponding menu;
- in the Settings menu, you can:
– change website Title, Tagline, Address, Time Zone in a General section;
– create Categories, Tags, change Post, Date and Time format on the website in the Writing section;
– track space used for Media uploads;
– adjust JetPack settings if you have it installed.
11. In the External part, you can check your website and log in to the actual wp-admin account via a browser on your phone by pressing the corresponding button. The last option ‘Remove Site’ will remove it from the WordPress App on your phone, the website itself will remain untouched.
You can also find the following options in the external part:
-
- My Sites. An option that allows you to manage your WordPress websites using this application. If you have more sites added to the app, you will be able to switch between them by pressing the websites’ buttons.
- Reader. By pressing it, you will be able to read some random WordPress articles created by other users.
- Publish post button
 allows publishing your posts.
allows publishing your posts.
- In Me menu you can change your profile settings and application settings.
- Notifications menu allows you to set up notifications that would be sent to your phone from your website.
That’s it!