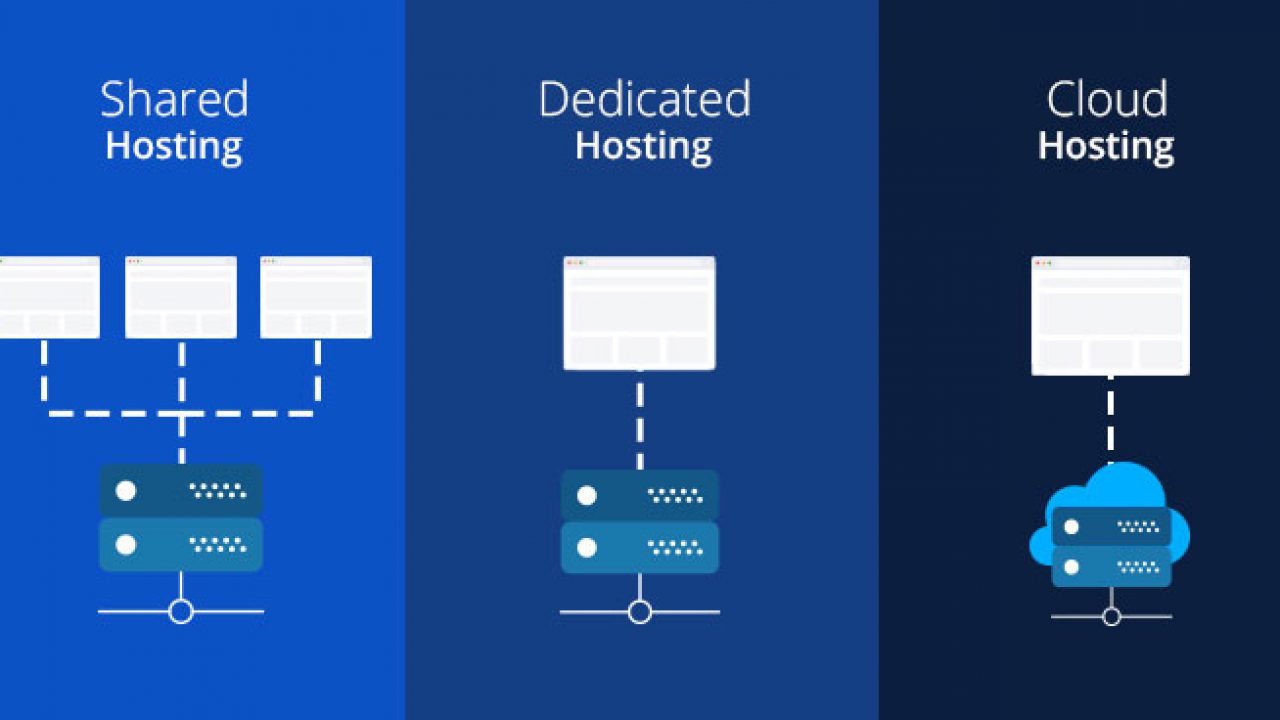
What is a Dedicated Server?
A dedicated server is a physical server that is dedicated to a single customer or organization, providing them with exclusive use of the server’s resources. This means that the customer has complete control over the server, including the ability to customize the operating system, install software, and configure the server to meet their specific needs.
A dedicated server is typically a high-performance server, often housed in a data center, and is managed by the customer or a third-party provider. Dedicated servers are often used by businesses, organizations, and individuals who require:
- High Performance: Dedicated servers are designed to provide high levels of performance, making them suitable for demanding applications such as e-commerce, gaming, and video streaming.
- Security: Dedicated servers provide a high level of security, as the customer has full control over the server and can implement robust security measures to protect their data.
- Customization: Dedicated servers can be customized to meet specific needs, such as installing custom software, configuring network settings, and selecting hardware components.
- Reliability: Dedicated servers are designed to be highly reliable, with redundant systems and backup power supplies to minimize downtime.
Types of dedicated servers:
- Physical Dedicated Server: A physical server located in a data center, managed by the customer or a third-party provider.
- Virtual Dedicated Server: A virtualized server running on a physical host machine, providing multiple virtual servers on a single physical machine.
- Cloud Dedicated Server: A cloud-based dedicated server, providing a virtualized environment with dedicated resources.
Features of dedicated servers:
- Root Access: Customers have full root access to the server, allowing them to customize and manage the operating system and software.
- Customizable: Dedicated servers can be customized with various hardware and software configurations to meet specific needs.
- Scalability: Dedicated servers can be easily scaled up or down as needed to accommodate changes in traffic or resource demands.
- 24/7 Support: Dedicated server providers typically offer 24/7 support for customers.
Benefits of dedicated servers:
- Increased Security: Dedicated servers provide a high level of security, as customers have full control over the server and can implement robust security measures.
- Improved Performance: Dedicated servers are designed to provide high levels of performance, making them suitable for demanding applications.
- Customization: Dedicated servers can be customized to meet specific needs, allowing customers to tailor their infrastructure to their unique requirements.
- Reliability: Dedicated servers are designed to be highly reliable, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
In summary, a dedicated server is a powerful computing resource that provides customers with exclusive use of a physical server, offering high performance, security, customization, and reliability.